
- Vectorise image illustrator how to#
- Vectorise image illustrator Pc#
- Vectorise image illustrator professional#
- Vectorise image illustrator mac#
- Vectorise image illustrator windows#
Adjusting the threshold, the number of colors, the paths, the corners, etc. If none of the presets gives you the desired result, further advanced options in the Image Trace panel give you greater control over the details.
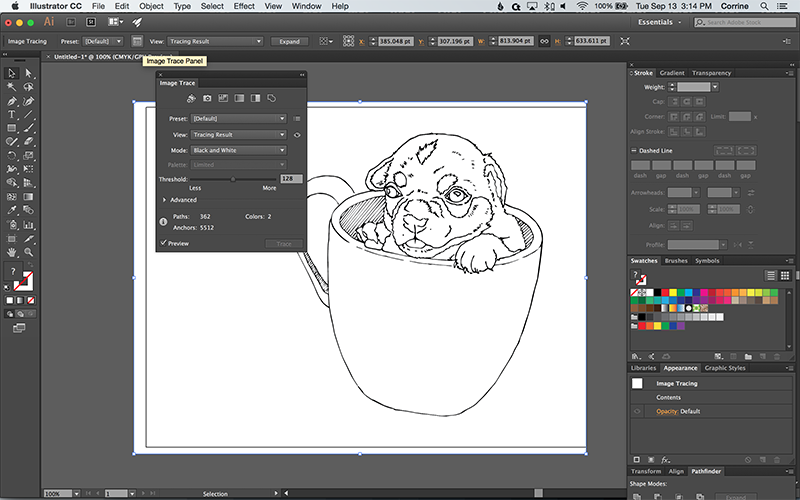
Every image is different, so you’ll have to play around with the settings to find the best fit. For instance, a detailed image will benefit from the High Fidelity Photo option, while you can use a limited color setting for a simple graphic. Selecting a suitable preset instantly adapts the vector settings to the nature of your image. The first and most important one is Presets. You’ll see a myriad of settings you can use to fine-tune the vectorization process in this panel. If you’re converting a colored image or simply need a bit more control over the presets, enable the Image Trace panel. However, this is merely scratching the surface when it comes to the capabilities of Illustrator’s Image Trace function. If you’re just converting a logo, you might not have to tweak anything and will still end up with a flawless vector graphic. The default settings work well for simple black and white images.
Vectorise image illustrator Pc#
Vectorise image illustrator how to#
Here’s how to use Image Trace in Adobe Illustrator on a PC: If tweaking the Image Trace settings doesn’t yield a perfect vector graphic, you can trace your image manually instead. This option will work well in most cases, with minimal adjustments needed. Illustrator is equipped with a handy Image Trace feature that makes turning raster images into vectors a breeze. How to Vectorize an Image in Illustrator on a PC When your image is ready, follow the steps below.

Crop your image so only the part you want to vectorize is included. If the image you want to convert doesn’t fit this profile, preparing it first will facilitate both your and the computer’s job later. Focusing your efforts on a single subject rather than a detailed landscape is a good idea.Ī PNG with a transparent background is a perfect candidate for vectorization, but a JPG with a single subject and a white background also performs well. Therefore, you’ll have better luck if you start out with a reasonably simple raster image. Vector images are usually used for logos and other simple graphics.
Vectorise image illustrator professional#
Although you can convert any image to vectors using Illustrator, not all images will yield equally professional results. Before You Beginīefore we open Illustrator and begin the vectorization process, let’s discuss the importance of the right kind of image for success. Read on to learn how to do so on several platforms.
Instead, you’ll need to vectorize your image in Illustrator.
Vectorise image illustrator windows#
Windows or other versions can look different.Vector graphics work completely differently from raster images, but simply clicking “Save as…” won’t be enough to leverage all their potential.
Vectorise image illustrator mac#
Note: the screenshots from this tutorial are taken from Adobe Illustrator CC Mac version. I’ll show you how to vectorize the image in two ways and the results can look totally different. The quickest and easiest option is definitely image trace, and you can do it from the Properties > Quick Actions panel.įor example, let’s make a vector from this pineapple image. You can turn a raster image into a vector image using the pen tool or image trace feature. There are many ways to make a vector image in Adobe Illustrator, but I’m going to put them in two main categories: vectorizing a raster image and making a vector from scratch. For example, it can be a shape, a traced image, outlined text, and a professional logo. When you create a design from scratch in Adobe Illustrator, it’s a vector unless you rasterize it. Basically, any editable images are vector images. Sounds confusing? Let me make it easier for you. Which means you can resize the image without losing resolution. A technical explanation would be: it’s an image made by mathematical formulas like points, lines, and curves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
